
Because email spam has become such a problem, email service providers such as Google, Microsoft, and Apple are becoming stricter about email authentication. Email authentication refers to checking if the senders of email are who they claim to be. If emails from your domain, including those sent from your website, aren't authenticated, they could be marked as spam or not delivered. Also, others will more easily be able to send emails that look like they're from your domain, by spoofing (faking) the sender address. This could trick your customers and prospects, harming your reputation. Fortunately, the email authentication protocols SPF, DKIM, and DMARC can help.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) allows you to specify the domains and IP addresses that are authorized to send email for your domain. For example, if you use Google for your email service, you'll need to include Google in your SPF record.
An SPF record is a DNS TXT record that looks like this:
v=spf1 include:_spf.domain1.com include:_spf.domain2.com ~allThis authorizes domain1.com and domain2.com to send email for your domain. The ~all is a soft fail (-all is a fail or hard fail). If you're using DMARC (which you should be), then it's better to use ~all, because -all may reject email that's relayed or forwarded, which is out of your control.
The services you want to authorize to send email for your domain should be able to tell you what to include in yours. You can find this in the service's documentation, or by searching for [service name] SPF, or by contacting the service's support.
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is used to digitally sign your email to prove that it came from your domain. You can authorize services to send mail for your domain. For example, the web host Flywheel sends email via SendGrid, so if your site is hosted by Flywheel and you want it to send email from your domain, you'll need to create DKIM records for SendGrid.
A DKIM record is a DNS TXT or CNAME record that looks like this:
s1.domainkey.u00000000.wl000.sendgrid.netThe services you want to authorize to send email for your domain should be able to tell you what records to create. You can find this info in the service's documentation, or by searching for [service name] DKIM, or by contacting the service's support.
Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) allows you to tell email servers that receive mail from your domain how strictly to handle authentication. There are 3 levels: none, quarantine, and reject.
A DMARC record is a DNS TXT record that looks like this:
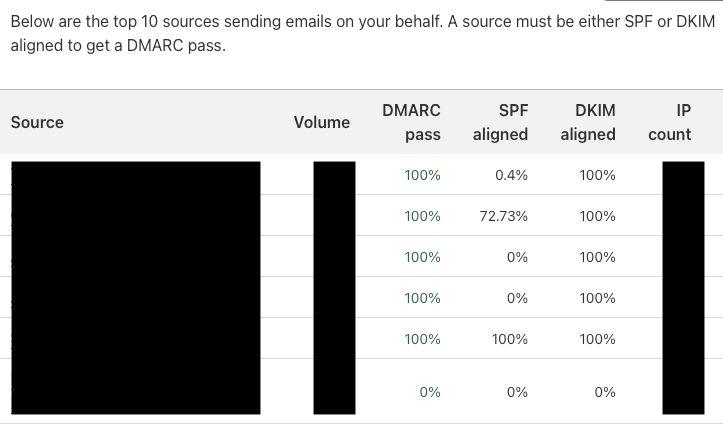
"v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua=mailto:[email protected]"This record is set to reject, and to email DMARC reports to [email protected]. These reports tell you if your emails are passing or failing SPF and DKIM checks. If services that should be authorized are failing, you should fix your records so they pass. You'll get a lot of emails that have .zip or .xml.gz attachments. It's a hassle to open these and look for records marked fail, so consider using a third-party service for this. You simply add their email address to your DMARC record, and they receive and monitor your DMARC reports. If you use Cloudflare for DNS, you can use their DMARC Management feature (currently in beta) for this.
To prevent email deliverability problems, it's best to use the quarantine policy for a period of time and monitor the DMARC reports before switching to the reject policy.
By default, WordPress uses wp_mail(), a PHP function, to send email. Your web host may send your site's email from an address on its own domain, rather than yours. In this case, your email authentication efforts will be wasted. You can ensure that your site's email is sent the way you want by configuring WordPress to send email via SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol).
Configuring how your WordPress site sends email is just one part of configuring and maintaining a WordPress site. If WordPress maintenance isn't how you like to spend your time, contact us about our WordPress Maintenance Service.
This article gives advice on how to make sure your emails reach people's inboxes instead of being marked as spam. It talks about SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, which are like security measures for emails. Following these tips can help make sure your emails get through properly. It's good to know about these things!
Thanks for reinforcing the article.